Are you looking for a reliable N52 Neodymium magnets manufacturer, are you searching for the strongest magnets for your application, or even expecting design for your own specificiation, I am glad you have come to the right place. With over 20 years design and manufacturing experience, AEMagnets is a lead Neodymium magnets supplier, serve to different industies, with various sizes and shapes. Applications from underwater to space, from normal temperature to high temperatures as over 200 degree, from louderspeaker to rotor, etc.
Are you eager to explore more about us, are you ready to discuss with us, let's start!

High grade N52 with diameter 10mm * 10

High grade N52, with size of 65*22*22

High grade N52, with size of OD 40mm * ID 25 * thickness 5mm
Neodymium magnets, also known as NdFeB, NIB, or Neo magnets, are a type of rare-earth magnet made from an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron to form the Nd2Fe14B tetragonal crystalline structure. They are the strongest type of permanent magnet commercially available, thereinto N52 is the top high grade in its category.
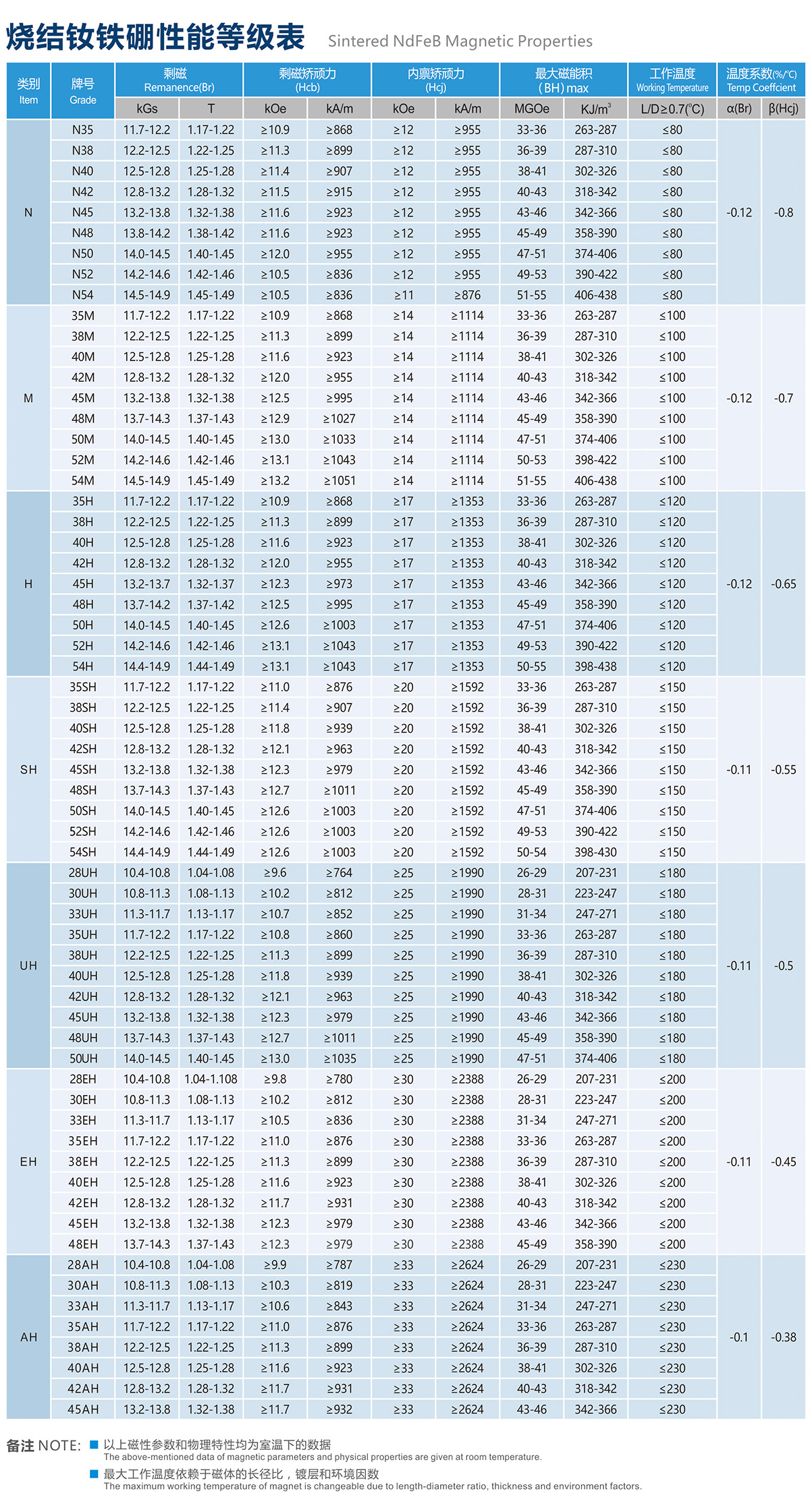
N52 Magnet Grade:
The "N52" designation specifically refers to the grade of the neodymium magnet. The grading system ranges from N35 to N52, with N52 being the highest, indicating a higher maximum energy product.
In the neodymium magnet grading system, the letter "N" stands for neodymium, and the number represents the maximum energy product in Mega-Gauss-Oersteds (MGOe). The higher the number, the stronger the magnet.
N52 magnets have a maximum energy product of 52 MGOe, making them one of the strongest commercially available neodymium magnets. These magnets are often chosen when a very high magnetic strength is required for a particular application.
Electronics: Neodymium magnets are widely used in electronic devices such as hard disk drives, headphones, and speakers due to their small size and high magnetic strength.
Motors and Generators: N52 magnets find extensive use in electric motors and generators, contributing to the efficiency and power of these devices.
Medical Devices: Neodymium magnets are utilized in various medical applications, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines and magnetic therapy devices.
Industrial Applications: N52 magnets are employed in industrial settings for tasks like metal separation in recycling plants, magnetic lifters, and in machining and manufacturing processes.
Consumer Products: These magnets are used in consumer products like magnetic clasps, closures for bags, and magnetic toys.
High Magnetic Strength: N52 magnets have an exceptionally high magnetic strength, making them suitable for applications that require a powerful magnetic field.
Compact Size: Despite their strength, neodymium magnets are relatively small and lightweight, which makes them ideal for applications where space is limited.
Cost-Effective: Neodymium magnets are cost-effective compared to other types of strong magnets, making them a popular choice for various applications.
Versatility: These magnets can be shaped into various forms, allowing for flexibility in design and application.
When using N52 magnets, it's crucial to consider these factors and follow safety guidelines to ensure proper handling and prevent accidents.
Brittleness: N52 magnets can be more brittle than lower-grade magnets, so they need to be handled with care to avoid chipping or breakage.
Corrosion: Neodymium magnets are prone to corrosion, so protective coatings are often applied to prevent degradation.
Temperature Sensitivity: Their magnetic properties can be sensitive to temperature variations, and high temperatures may cause a reduction in magnet strength.
When using N52 magnets, it's crucial to consider these factors and follow safety guidelines to ensure proper handling and prevent accidents.
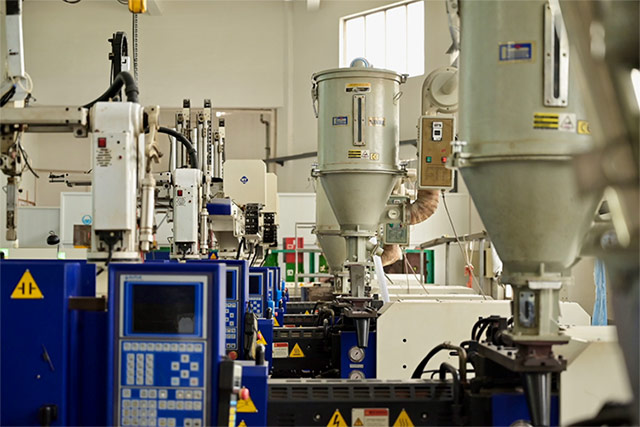

Beyond Neodymium, our material expertise spans a diverse range, incorporating cutting-edge alloys and composites. We harness materials with precision to craft solutions that meet the unique demands of modern applications.
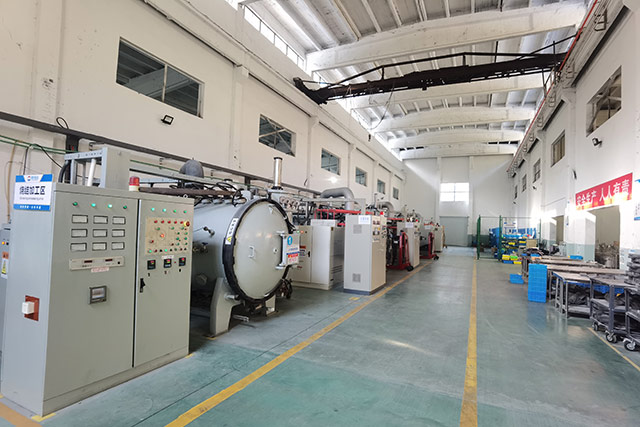

Recognizing the varied needs of industries, we offer more than off-the-shelf products. Our customization prowess allows us to tailor magnetic solutions, optimizing size, shape, and magnetic strength to align seamlessly with specific project requirements.
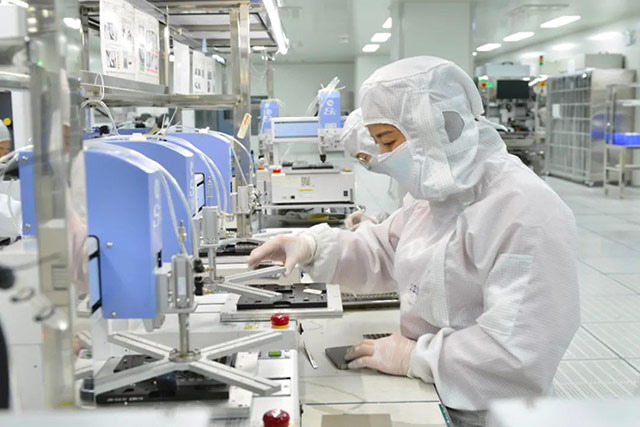

We are not merely suppliers but collaborators in innovation. Our team works closely with clients to integrate magnetic solutions seamlessly into their designs. From automotive applications to medical devices, our magnets are seamlessly woven into the fabric of modern technological advancements.
Adapting to the ever-evolving landscape of industry challenges, we stay at the forefront of research and development. Our commitment to staying abreast of emerging technologies ensures that our solutions remain not only current but also ahead of the curve.
Let us be your partner in magnets supply chain
AEMagnets is focus on creating values for our customer with innovative solution, supporting various industries through advanced magnetic technology.
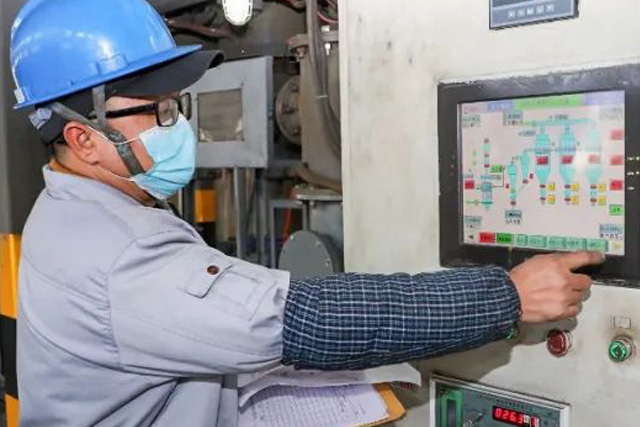

With 20 years of technical magnet expertise, AEMagnets is uniquely qualified in all aspects of magnets engineering and manufacturing. We will work with our customer to achieve an optimized magnetic solution for virtually any need focus on quality, application, cost, lead time. Engineering is core of our business. We've found that concurrent engineering from early start of a project yields the best overall results, which is why we like to work with our customers from the very beginning on major projects by utilizing our highly-skilled technical experts, in our company we call it Early Involvement of Engineering(EIE).

As a licensed and certified magnet manufacturer, we use high level inspection equipment and testing methods to ensure that our supplied products can meet customer requirements. Besides we also conduct quality planning from very beginning as to mitigate risk from virtual to real production. If there is complaint happened we will treat serious and use 8D methodology to make a thoroughly investigation and also set preventive actions, by insist on this our quality keeps on a very high level, which will finally return back to our customer's trust.
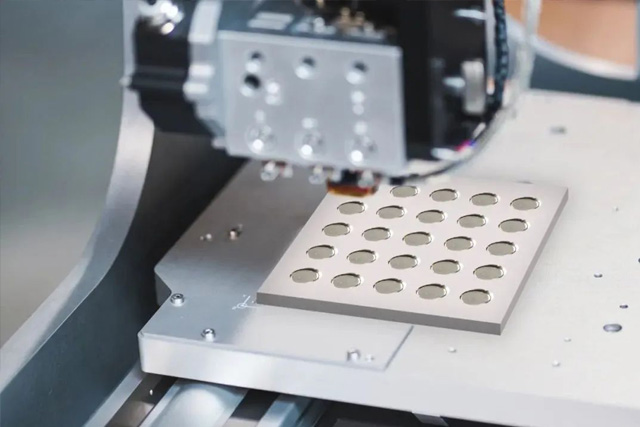

Insist to pursue continuous improvement for cost management through lean production & supply chain management, etc., keep price competitive and share interests with customer.
Neodymium magnets, as the 2nd generation of rare earth magnets(the 1 st generation is Samarium Cobalt Magnets) which was discovered independently in 1984 by General Motors and Sumitomo Special Metals. Neodymium magnets well known as NdFeB magnets, made from an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron. They are the most widely used type of rare-earth magnet and the strongest of permanent magnet available commercially.
Due to their exceptional magnetic properties Neodymium magnets are a key component in various applications.
Neodymium magnets, also known as NdFeB magnets, are composed of an alloy primarily made of three elements: neodymium (Nd), iron (Fe), and boron (B). The combination of these elements creates a powerful permanent magnet with exceptional magnetic properties. The typical composition of neodymium magnets, is approximately as follows:
Neodymium (Nd): About 29-32% by atomic percent.
Iron (Fe): About 63-68% by atomic percent.
Boron (B): About 1-1.5% by atomic percent
Neodymium magnets are classified into different grades, denoted by the letter 'N' followed by a number. Higher numbers indicate stronger magnets. For example, an N52 magnet is stronger than an N35 magnet. Sometimes after the number there will be a letter, like N38EH, EH stands for extra high, means can work under high temperure as 200 degree.
Yes, neodymium magnets typically require plating to protect them from corrosion and improve their overall durability. Neodymium magnets are made of a compound that includes iron, and iron is prone to corrosion when exposed to moisture or harsh environmental conditions. Plating serves several essential purposes for neodymium magnets:
Corrosion Resistance:
The most critical reason for plating neodymium magnets is to provide a protective layer that prevents corrosion. Without plating, the iron content in the neodymium magnet is susceptible to rusting, which can degrade the magnet's performance over time.
Environmental Protection:
Plating acts as a barrier against environmental elements, including moisture and chemicals. This protection is crucial for applications where magnets are exposed to various conditions, such as in automotive, marine, or outdoor settings.
The choice of plating material depends on the specific requirements of the application. Nickel-copper-nickel is a commonly used plating for neodymium magnets due to its excellent corrosion resistance. However, other coatings may be chosen based on factors like cost, aesthetics, or unique environmental considerations.
In summary, while neodymium magnets do not inherently resist corrosion, proper plating is crucial to ensure their long-term performance and functionality in various applications.
Two common methods are used to measure the magnetic strength of magnets: Gauss testing and Pull testing.
Gauss Testing: Gauss measurement gauges a magnet's field strength using a device called a gauss meter.
Pull Testing: This method measures the force required to detach a known ferrous object from the magnet's surface.
The choice between these methods depends on the specific requirements of the application and the accuracy needed. Pull testing is often preferred for its practicality and ease of use, especially in scenarios where reliability and repeatability are crucial, such as in quality control programs.
Rarely, Neodymium magnets are the most permanent magnets in the world. As long as you don't overheat them, they lose less than 1% of their strength every 10 years. With daily use, you basically don’t feel any changes
Yes, Neodymium magnets may demagnetize under the following conditions:
From a medical point of view, neodymium magnets are not harmful to the human body. Moreover, the use of rare earth magnets for magnetic therapy is very common in the medical field. However, if the human body carries medical electronic equipment such as a pacemaker, it is strongly recommended to avoid contact with powerful neodymium magnets, as this may cause serious harm to health. Be aware of potential allergies to the materials used in neodymium magnets, such as nickel. If irritation occurs, discontinue direct skin contact and seek medical advice immediately.











Neodymium magnets, as the 2nd generation of rare earth magnets(the 1 st generation is Samarium Cobalt Magnets) which was discovered independently in 1984 by General Motors and Sumitomo Special Metals.
Neodymium magnets well known as NdFeB magnets, made from an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron. They are the most widely used type of rare-earth magnet and the strongest of permanent magnet available commercially.
Due to their exceptional magnetic properties Neodymium magnets are a key component in various applications.

Neodymium magnets find versatile applications across various domains, owing to their exceptional magnetic properties and stability. The key applications include:
Electronics and Communication Equipment
Utilized as heat dissipation materials for CPUs in electronic computers and communication equipment, effectively reducing working temperatures and extending service life.
Manufacturing of Permanent Magnets
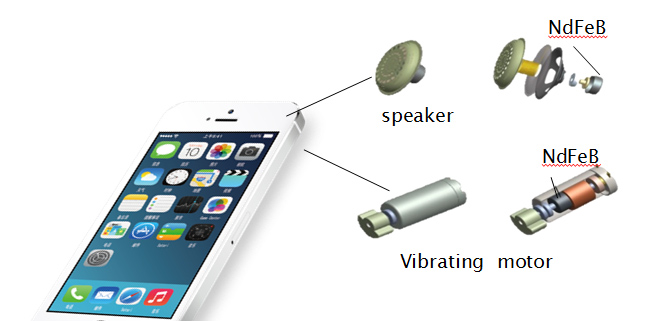
Widely employed in manufacturing permanent magnets for applications such as magnetic resonance coils, magnetic tape recorders, circular polaritons for optical fibers, ultra-small speakers, and magnetic drums in recorders.
Electroacoustic Transducers
Used in electroacoustic transducers to replace steel springs in machine receivers, reduce volume and weight; replace paper pots in television mufflers to reduce noise; substitute traditional cylindrical speakers with soft electromagnets in audio equipment to enhance effective volume; employ soft magnetic thin film transistors (TFTs) for large screen color display boards in computer monitors; contribute to reverse radar devices in cars; integrate into gyroscope systems on aircraft; and serve as switches for controlling motor speed in electric shavers.
Connecting Device Between Strong and Weak Electricity
Functions as a connecting device between strong and weak electricity in various electronic applications.
Hall Elements for Sensors and Actuators
Utilized in the manufacture of Hall elements for diverse sensors and actuators, including automotive speedometers, tachometers, and odometers.
Magnetic Recorders
Employed as magnetic recorders in computer disk drives, tape recorders, and automatic players.
Motor Manufacturing
Used in the manufacturing of motor commutators and micro motors, contributing to the efficiency of motor-driven systems.
Coil Winding Materials
Serves as winding materials for speaker coils and headphone coils in audio equipment, as well as packaging materials for TV tube glass shells.
In conclusion, the widespread use of neodymium iron boron magnetic materials spans electronics, communication, manufacturing, sensors, actuators, and motors, showcasing their adaptability and reliability in various technological applications.
High Magnetic Performance: Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) is currently the second-highest-performing permanent magnet after absolute zero holmium magnets. It possesses a high magnetic energy product and high residual magnetism, capable of generating magnetic fields similar to many other materials.
Small Volume, Light Weight: Due to its high magnetic strength, only a small amount of neodymium magnetic material is needed in the application process to generate a magnetic field similar to that of many other materials. This significantly reduces product volume and weight.
Strong Stability, High Efficiency: neodymium magnetic materials exhibit excellent resistance to magnetic loss and can operate stably in high-temperature environments. The working temperature limit of ordinary magnetic materials is approximately around 80°C, beyond which severe demagnetization occurs, affecting product performance. In contrast, neodymium magnetic materials can have a maximum working temperature of up to 220°C. Although there is still a gap compared to samarium cobalt magnets in terms of high-temperature resistance, considering production capacity and cost, neodymium magnetic materials are a preferable choice.
Cost-Effective: In comparison to samarium cobalt magnets, another rare-earth magnet of similar strength, neodymium iron boron magnets are more cost-effective, providing a significant advantage.
Strong Machinability: neodymium magnets can be shaped for specific purposes through mechanical processing, including the production of small batches for samples. Even in small sizes, they can exhibit high magnetic performance.
Wide Range of Applications: neodymium magnets find application in virtually every industry, making their presence ubiquitous.
In conclusion, as an excellent permanent magnetic material, neodymium iron boron possesses characteristics such as high magnetism, small volume, light weight, strong stability, cost-effectiveness, and excellent machinability. These qualities have led to its widespread application in various fields.
lf you're looking for Neodymium Magnets, we'll work with you to find the best option for your appilaction.

When considering the purchase of Neodymium magnets, several factors should be taken into account to ensure that the selected magnets meet the specific requirements of your application.
Here are some key factors to consider: Size and Shape, Magnetic Strength (Grade), Operating Temperature, Magnetization direction, Coating.

Gauss Testing
Gauss measurement gauges a magnet's field strength using a device called a gauss meter.
Process: A handheld probe of the gauss meter is moved around the magnet, and the values increase or decrease accordingly.
Limitations: Gauss meters are highly sensitive, making it challenging to obtain reliable, repeatable values. Calibration issues are common, and even slight movements of the probe can yield different results.
Application: Provides insights into a magnet's circuit design and field gradient but may not be the preferred method due to its sensitivity.

Normally the neodymium magnets can be shipped by air, sea, railway, land, depends on weight and distance, before shipping the magnets need to be packed with magnetic shield to make sure the magnetism can not affect outside of the package. Magnetic inspection is necessary for air shipping which is conducted by 3rd party, meanswhile MSDS report is necessary for sea shipping.

Navigating the realm of neodymium magnets can be overwhelming, especially for newcomers. Yet, with invaluable insights into neodymium magnets, the complexity of selection transforms into a streamlined process.
Backed by decades of expertise in the neodymium magnets sector, AEMagnets stands as a reliable source for optimal materials grades, size, shapes, and specifications catering to projects of any scale. Our dedicated team is ready to provide insightful guidance, with the added convenience of customizable samples meticulously crafted to suit your distinct requirements. Trust in AEMagnets for a seamless neodymium magnets selection experience.

